Windows Server Ports
Review a full list of protocols and ports required for Netwrix Auditor for Windows Server.
- Allow outbound connections from the dynamic (1024 - 65535) local port on the computer where Netwrix Auditor Server resides.
- Allow outbound connections to remote ports on the source and inbound connections to local ports on the target.
Tip for reading the table: For example, on the computer where Netwrix Auditor Server resides (source), allow outbound connections to remote 139 TCP port. On monitored computers (target), allow inbound connections to local 139 TCP port.
| Port | Protocol | Source | Target | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 139 445 | TCP | Netwrix Auditor Server | Monitored computer | Service Control Manager Remote Protocol (RPC) Remote registry |
| 135 + Dynamic: 1024 -65535 | TCP | Netwrix Auditor Server | Monitored computer | Windows Management Instrumentation Collect objects |
| 135 + Dynamic: 1024 -65535 | TCP | Netwrix Auditor Server | Monitored computer | Collect removable storage insertions. Allow the following process to use the port: %systemroot%\system32\plasrv.exe |
| 135 | TCP | Netwrix Auditor Server | Monitored computer | Service Control Manager Remote Protocol (RPC) Core Service installation |
| 137 through 139 | UDP | Netwrix Auditor Server | Monitored computer | Service Control Manager Remote Protocol (RPC) Core Service installation |
| 445 | TCP | Netwrix Auditor Server | Monitored computer | SMB 2.0/3.0 |
| 9011 | TCP | Computers where Netwrix Auditor for Windows Server Compression Services reside | Netwrix Auditor Server | Network traffic compression and interaction with services |
Configure Windows Firewall Inbound Connection Rules
You can also configure Windows Firewall settings through Group Policy settings. To do this, edit the GPO affecting your firewall settings. Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network >Network Connections > Windows Firewall, select Domain Profile or Standard Profile. Then, enable the Allow inbound remote administration exception.
Step 1 – On each audited server, navigate to Start > Control Panel and select Windows Firewall.
Step 2 – In the Help Protect your computer with Windows Firewall page, click Advanced settings on the left.
Step 3 – In the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security dialog, select Inbound Rules on the left.
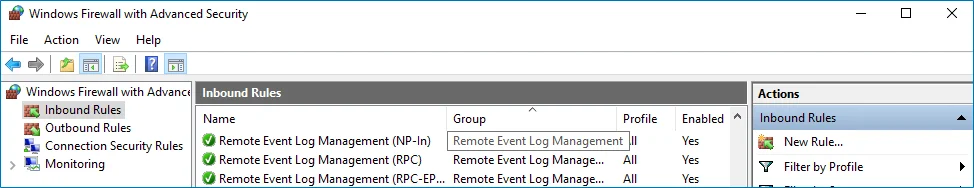
Step 4 – Enable the following inbound connection rules:
- Remote Event Log Management (NP-In)
- Remote Event Log Management (RPC)
- Remote Event Log Management (RPC-EPMAP)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (ASync-In)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-In)
- Network Discovery (NB-Name-In)
- File and Printer Sharing (NB-Name-In)
- File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv4-In)
- File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv6-In)
- Remote Service Management (NP-In)
- Remote Service Management (RPC)
- Performance Logs and Alerts (DCOM-In)
- Performance Logs and Alerts (Tcp-In)
If you plan to audit Windows Server 2019 or Windows 10 Update 1803 without network compression service, make sure the following inbound connection rules are enabled:
- Remote Scheduled Tasks Management (RPC)
- Remote Scheduled Tasks Management (RPC-EMAP)