Permissions for SQL Server Auditing
Before you start creating a monitoring plan to audit your SQL Server, plan for the account that will be used for data collection – it should meet the requirements listed below. Then you will provide this account in the monitoring plan wizard.
Starting with version 9.96, you can use group Managed Service Accounts (gMSA) as data collecting accounts.
On the target SQL Server:
- To access SQL Server, Windows authentication will be used, so data collection account should be a Windows account specified in the domain\user format (domain\user$ for Managed Service Account). SQL Server logins and authentication method are not supported.
- The account must be assigned the System Administrator server role for this SQL Server. See Assigning 'System Administrator' Role section for more information.
- For auditing SQL Server availability on groups, the account must have the sysadmin server role granted on each server added to an availability group.
- If you plan to collect state-in-time data from SQL Server, in addition to requirements above the
account will also need:
- Local Administrator rights on the target SQL Server.
- If SQL Server is included in the Active Directory domain, the account should also be included in that domain.
Assigning 'System Administrator' Role
-
On the computer where audited SQL Server instance is installed, navigate to Start → All Programs → Microsoft SQL Server → SQL Server Management Studio.
-
Connect to the SQL Server instance.
-
In the left pane, expand the Security node. Right-click the Logins node and select New Login from the pop-up menu.
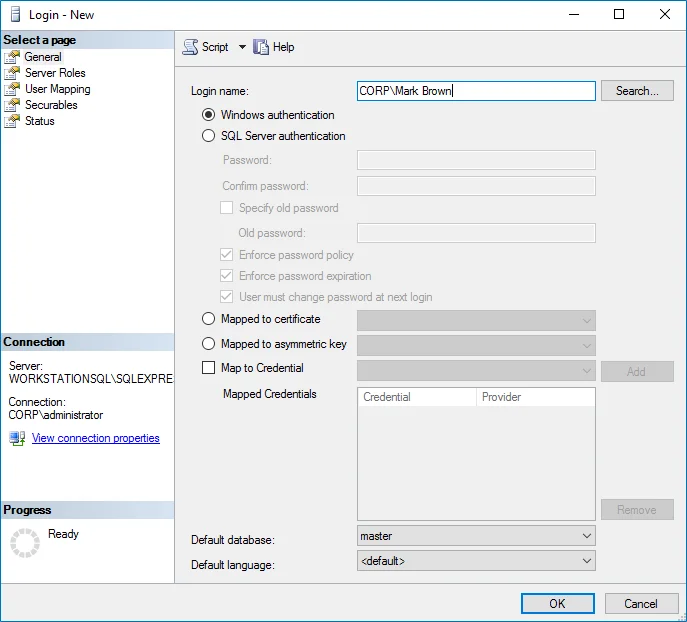
-
Click Search next to Login Name and specify the user that you want to assign the sysadmin role to.
-
Specify the Server roles tab and assign the sysadmin role to the new login.