Permissions for Exchange Auditing
Before creating a monitoring plan to audit your Exchange server, you need to plan for the account that will be used for data collection. This account should meet the requirements listed below. You will specify this account in the monitoring plan wizard (or in the monitored item settings).
Account Requirements
The account used for data collection must meet the following requirements:
-
Member of the Domain Admins group on the target server.
NOTE: This covers all the required permissions below and is a mandatory setting if you want to use network traffic compression for data collection.
OR
-
The combination of the following rights and permissions if you plan to disable network traffic compression for your monitoring plan or, for some reasons, do not want to add this account to the Domain Admins group:
- The Manage auditing and security log policy must be defined for this account. See the Permissions for Active Directory Auditing topic for additional information.
- If you plan to process the Active Directory Deleted Objects container, Read permission on this container is required. See the Permissions for Active Directory Auditing topic for additional information.
- The account must belong to the Organization Management or Records Management group. See the Add Account to the Organization Management Group topic for additional information.
- Several management roles assigned: Audit Logs role, View-only Configuration role, Mail Recipients role, and Monitoring role. See the Add Account to the Organization Management Group topic for additional information on how to perform role assignment.
- Additional configuration if auto-backup is enabled for the domain controller event logs (see below).
Additional Configuration for Domain Controller's Event Logs Auto-backup
The following is required if auto-backup is enabled for the domain controller event logs:
- Permissions to access the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\Security registry key on the domain controllers in the target domain. See the Assign Permission to Read the Registry Key topic for additional information.
- Membership in one of the following groups: Administrators, Print Operators, Server Operators
- Read/Write share permission and Full control security permission on the logs backup folder
Add Account to the Organization Management Group
Follow the steps to add account to the Organization Management group.
Step 1 – Navigate to Start > Active Directory Users and Computers on any domain controller in the root domain of the forest where Microsoft Exchange 2019, 2016, or 2013 is installed.
Step 2 – In the left pane, navigate to <domain_name> > Microsoft Exchange Security Groups.
Step 3 – On the right, locate the Organization Management group and double-click it.
Step 4 – In the Organization Management Properties dialog that opens, select the Members tab and click Add.
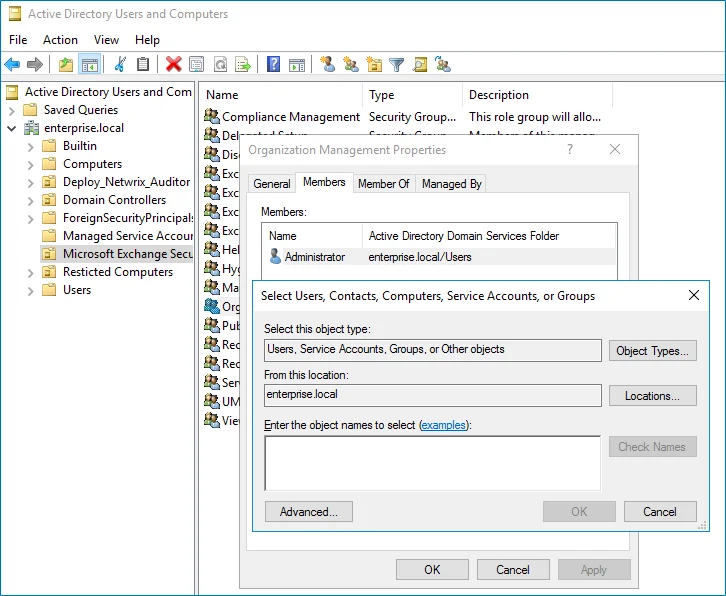
If for some reason you do not want this account to belong to the Organization Management group, you can add it to the Records Management group in the same way. The Records Management group is less powerful, and accounts belonging to it have fewer rights and permissions.
Assign Management Roles
Perform this procedure only if the account selected for data collection is not a member of the Organization Management or the Records Management group.
Follow the steps to assign management roles.
Step 1 – On the computer where Microsoft Exchange 2019, 2016, 2013 or is installed, open the Exchange Management Shell under an account that belongs to the Organization Management group.
Step 2 – Use the following syntax to assign the required management role to a user:
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Name <assignment name> -User <UserName> -Role <role name>
For example:
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Name "AuditLogsNetwrixRole" -User Corp\jsmith -Role "Audit Logs"
In this example, the user CORP\jsmith has been assigned the Audit Logs role.
Assign Permission to Read the Registry Key
This permission is required only if the account selected for data collection is not a member of the Domain Admins group.
This permission should be assigned on each domain controller in the audited domain, so if your domain contains multiple domain controllers, it is recommended to assign permissions through Group Policy, or automatically using Audit Configuration Assistant.
To assign permissions manually, use the Registry Editor snap-in or the Group Policy Management console.
Assign Permission Via the Registry Editor Snap-in
Follow the steps to assign permission via the Registry Editor snap-in.
Step 1 – On your target server, open Registry Editor: navigate to Start > Run and type "regedit".
Step 2 – In the left pane, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControl Set\Services\EventLog\Security.
Step 3 – Right-click the Security node and select Permissions from the pop-up menu.
Step 4 – Click Add and enter the name of the user that you want to grant permissions to.
Step 5 – Check Allow next to the Read permission.
Step 6 – For auditing Logon Activity, you also need to assign the Read permission to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SECURITY\Policy\PolAdtEv registry key.
Assign Permission Using the Group Policy Management Console
Follow the steps to assign permission using the Group Policy Management console.
Step 1 – Open the Group Policy Management console on any domain controller in the target domain: navigate to Start > Windows Administrative Tools (Windows Server 2016/2019) or Administrative Tools (Windows 2012 R2 and below) > Group Policy Management.
Step 2 – In the left pane, navigate to Forest: <forest name> > Domains > <domain name> >
Domain Controllers. Right-click the effective domain controllers policy (by default, it is the
Default Domain Controllers Policy), and select Edit .
Step 3 – In the Group Policy Management Editor dialog, expand the Computer Configuration node on the left and navigate to Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Registry.
Step 4 – Right-click in the pane and select Add Key.
Step 5 – Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SECURITY\Policy\PolAdtEv and click OK.
Step 6 – Click Add and enter the name of the user that you want to grant permissions to and press Enter.
Step 7 – Check Allow next to the "Read" permission and click OK
Step 8 – In the pop-up window, select Propagate inheritable permissions to all subkeys and click OK.
Step 9 – Repeat the steps 4-8 for keys below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurePipeServers\winreg;HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\Security.
Step 10 – Close Group Policy Management console.
Step 11 – Navigate to Start > Run and type "cmd". Input the gpupdate /force command and
press Enter. The group policy will be updated.
Step 12 – Type repadmin /syncall command and press Enter for replicate GPO changes to other
domain controllers.
Step 13 – Ensure that new GPO settings were applied to the domain controllers.