Azure Files Activity Auditing Configuration
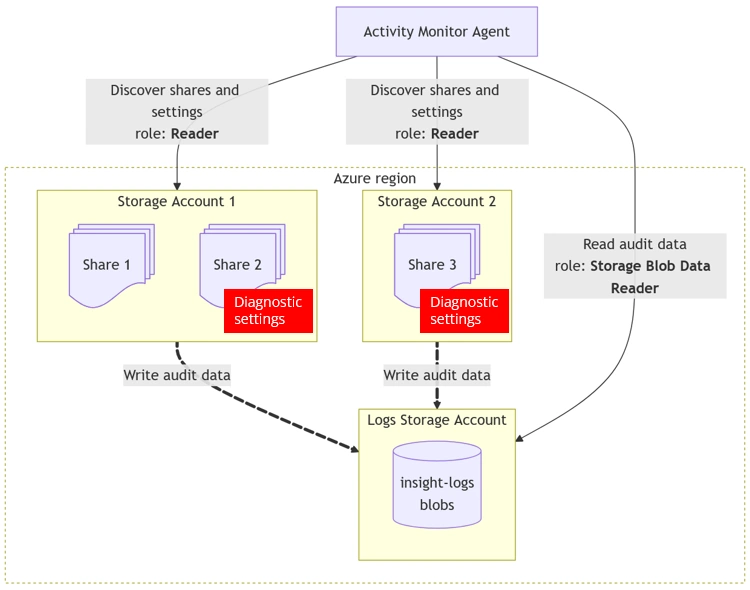
Activity Monitor can monitor CIFS activity on Azure Files shares.
The product uses the native auditing capability of Azure Files, which writes audit data to a separate storage account.
This feature requires manual configuration.
There are several steps in preparing Azure Files for monitoring:
- Enable auditing for storage accounts.
- Register an application in Azure.
- Assign permissions and RBAC roles.
- Configure Activity Monitor.
Enable auditing for storage accounts
Auditing in Azure Files is disabled by default. It must be enabled for each storage account to be monitored.
Logs storage account
You must provide a storage account for audit data. The audit data is written as blobs named insight-logs to that storage account.
It must be a different storage account — it cannot be the same account that hosts Azure Files.
It is recommended to share such a logs storage account among multiple files storage accounts.
A single account can store nearly unlimited blobs and up to 5 PB of data, which is more than enough for audit logs.
A shared account also helps stay within the Azure limit of 250–500 accounts per region per subscription.
However, for security reasons, you may choose to use separate logs storage accounts so that activity from different accounts is not mixed in the same blob storage.
The logs storage account must be in the same Azure region as the monitored Azure Files storage account, but it does not need to be in the same resource group or subscription.
Because the product does not require historical logs, it is recommended to configure an Azure Lifecycle Management rule for this storage account
to control storage volume and cost (not documented here). Otherwise, the data will be stored indefinitely.
Diagnostic setting
To enable auditing, you must enable the Diagnostic Setting for each Azure Files storage account to be monitored.
This can be done for each storage account individually or in bulk using Azure Policy to set Diagnostic Settings
at the management group, subscription, or resource group scope (not documented here).
-
Open the storage account in the Microsoft Azure portal.
Navigate to Monitoring > Diagnostic settings > File. -
Click Add diagnostic setting to create a new auditing configuration or open an existing one.
-
Under the Logs section, select audit, StorageRead, StorageWrite, and StorageDelete.
You can adjust these categories based on your needs; for example, unselect StorageRead if you are not interested in read activity. -
Under the Destination details section, select Archive to a storage account, then choose the storage account prepared in Step 1.
-
Click Save to apply the diagnostic changes.
It may take up to 90 minutes for the changes to take effect.
Register an application in Azure
Monitoring of Azure Files requires an application to be registered in the Azure portal, assigning it permissions to access the Graph API and
RBAC roles to access storage accounts.
A user account with the Global Administrator role is required to register an app and grant admin consent in Microsoft Azure.
If you already have an application registered for Activity Monitor for Entra ID, SharePoint Online, or Exchange Online, you can reuse that
registration for Azure Files by assigning additional RBAC roles.
Follow these steps to register the application in Azure.
Open Microsoft Azure portal
- Azure Public – https://portal.azure.com/
- Azure for US Government GCC – https://portal.azure.com/
- Azure for US Government GCC High – https://portal.azure.us/
- Azure for US Government DoD – https://portal.azure.us/
- Azure Germany – https://portal.microsoftazure.de/
- Azure China by 21Vianet – https://portal.azure.cn/
Use the search box to locate the App registrations page, then select New registration.
Register an application
- Specify Netwrix Activity Monitor as the application name.
- Choose Accounts in this organizational directory only.
- Change the type of Redirect URI to Public client/native (mobile & desktop).
- Specify
urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oobas the value. - Click Register.
Copy Application (client) ID and Tenant (directory) ID
On the Overview page, copy the Application (client) ID and Directory (tenant) ID values and save them for later.
Create a new client secret
- Open the Manage > Certificates & secrets page.
- Select New client secret.
- Specify a description and an expiration period.
- On the Certificates & secrets page, copy the Value of the created secret and save it for later.
Be aware of the client secret's expiration date. You'll need to generate a new one before it expires to ensure uninterrupted monitoring.
Make sure you copy the Value, not the Secret ID.
Grant API permissions
Activity Monitor requires the User.Read.All permission to resolve user SIDs in activity events to user names.
- Open the API permissions page.
- Select Add a permission and add the following to the existing User.Read:
Microsoft Graph
Type: Application permissions
Permission:User.Read.All - Click Grant admin consent for [tenant name], then confirm when prompted.
This action requires a Global Administrator.
Assign Azure RBAC roles for storage accounts
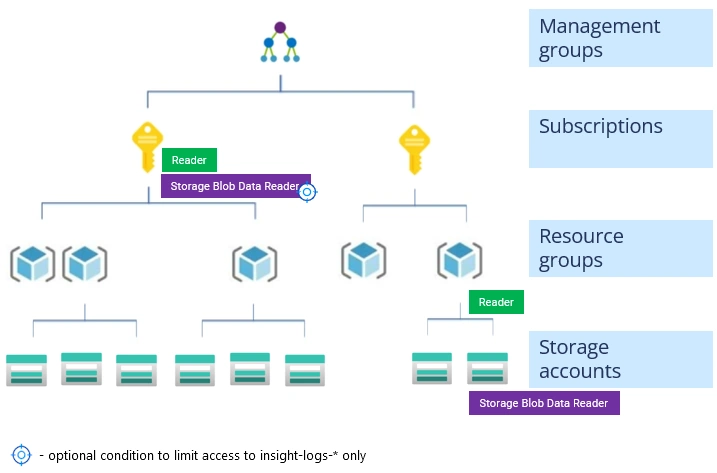
The registered application requires Azure RBAC role assignments to list storage accounts and read audit data.
Assign the following roles to the registered application:
-
Reader– the management plane role.
Allows enumeration of storage accounts and reading of their settings. -
Storage Blob Data Reader– the data plane role.
Allows reading of audit data from the logs storage account(s).
You can assign these roles at different levels, which grant access to all storage accounts within the selected scope:
- Management group – grants access to all storage accounts under the management group.
- Subscription – grants access to all storage accounts under the subscription.
- Resource group – grants access to all storage accounts under the resource group.
- Storage account – grants access to the specified storage account only.
Choose the appropriate scope, and then follow these steps:
- In the Azure portal, open the target scope resource (management group, subscription, resource group, or storage account).
- Open the Access control (IAM) page.
- Select Add > Add role assignment.
- Select
Readeron the Role page, and then select Next. - Select the registered application on the Members page, and then select Review + assign.
- Select Add > Add role assignment again.
- Select
Storage Blob Data Readeron the Role page, and then select Next. - Select the registered application on the Members page, and then select Next.
- (Optional) Select Add condition on the Conditions page, change the editor type to Code, and enter the following:
(
(
!(ActionMatches{'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read'})
)
OR
(
@Resource[Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers:name] StringStartsWith 'insights-logs-'
)
)
This condition grants access only to blob containers that store audit data. Access to all other containers is denied.
- Select Review + assign.
It may take some time for the RBAC assignments to become effective.
Configure Activity Monitor
The last step is adding the Azure Files storage account to Activity Monitor.
- On the Monitored Hosts & Services page, select Add Host/Service.
- Select the agent that will be monitoring Azure Files, and then select Next.
- Select Azure Files, specify the tenant’s domain name, and then select Next.
- On the Connection page, specify the Tenant ID (if it was not resolved automatically), Client ID, and Client Secret—values
copied in the previous steps during application registration. - Select Connect.
The button will verify the connection to Azure, enumerate all storage accounts, and retrieve their settings visible to the registered application.
If the product fails to enumerate storage accounts, the RBAC roles were either assigned incorrectly or have not yet become effective. Retry later.
- On the Storage Accounts page, select the storage accounts to be monitored, and then select Next.
- Complete the wizard by selecting operations and output settings.
You can use this wizard multiple times to add newly created storage accounts—already added accounts will be ignored.
- Check the status of the added storage accounts on the Monitored Hosts & Services page.
Address any audit setting misconfigurations or missing RBAC roles.